Adolescence (10–19 years) is the most crucial period in a growing child’s life. It can be normal in many cases where the children grow and mature physically, mentally and emotionally ,but sometimes it can very turbulent for some children. According to WHO , One in six people are aged 10–19 years.
- Mental health conditions account for 16% of the global burden of disease and injury in people aged 10–19 years.
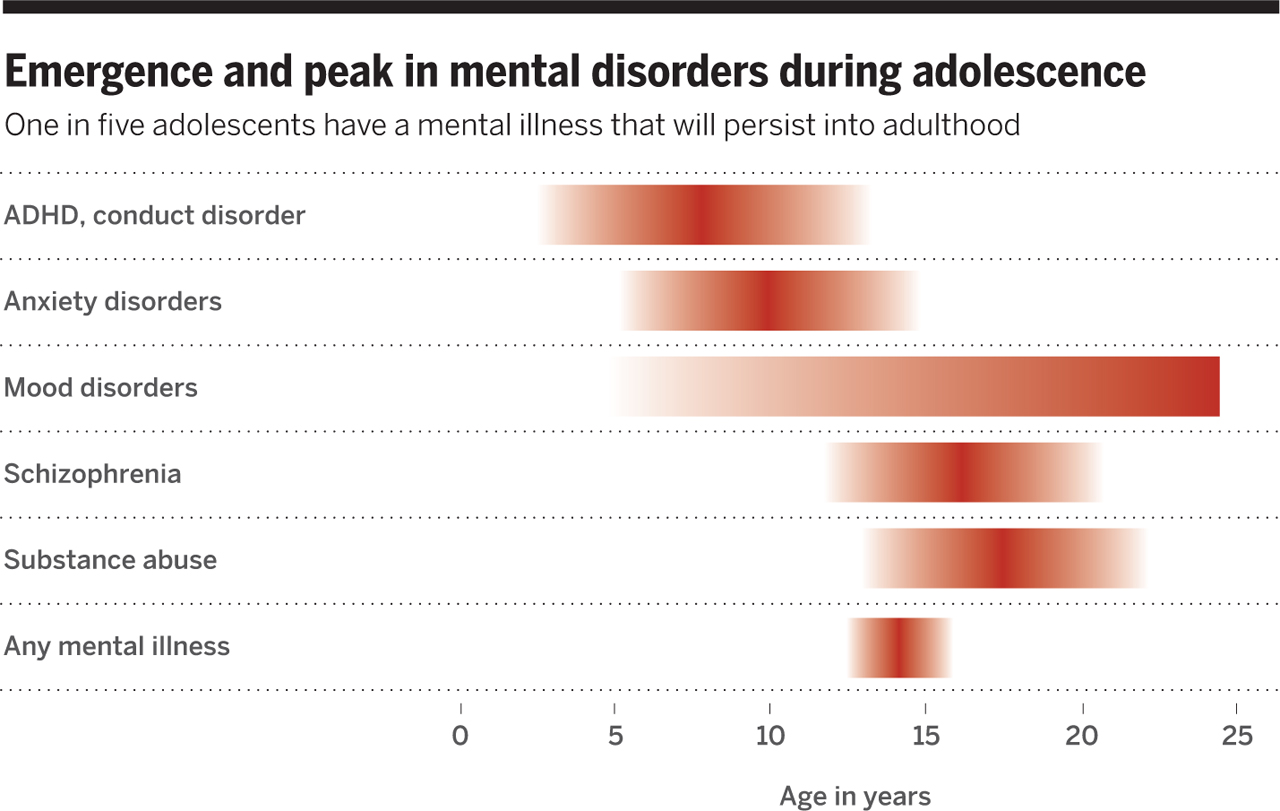
- Half of all mental health conditions start by 14 years of age but most cases are undetected and untreated.
- Globally, depression is one of the leading causes of illness and disability among adolescents.
- Suicide is the third leading cause of death in 15–19 year olds.
- The consequences of not addressing adolescent mental health conditions extend to adulthood, impairing both physical and mental health and limiting opportunities to lead fulfilling lives as adults.
- Mental health promotion and prevention are key to helping adolescents thrive.
- Worldwide, it is estimated that 10–20% of adolescents experience mental health conditions, yet these remain under diagnosed and under treated. Signs of poor mental health can be overlooked for a number of reasons, such as a lack of knowledge or awareness about mental health among health workers, or stigma preventing them from seeking help.
Mental health determinants for adolescents: Adolescence has been considered to be the foundation of a persons life where they get to formulate and maintain many social and emotional habits which are important not only for their physical well being but also for their mental well being.
Stress has an immense impact on an adolescent’s life. An adolescent who can cope adaptively with the stressors he has to face, can move on in happily in life. Sometimes many adolescents are not able to cope well and buckle under the pressures they have to face and turn to maladaptive coping strategies like indulging in drugs or risky behaviors.
Media has a tremendous influence on our youth. It is like a double edged sword, where it imparts ready and easy solutions to many academic and technical problems they face. But it also paints a ‘larger than thou picture’ for our adolescents who get confused between the reel and the real life. This can also affect their perceptions or aspirations for their future.
The Quality of their home life and their relationships with their parents and siblings are other important determinants for their mental health.
Violence (including harsh or negligent parenting and bullying), physical abuse or a history of Child or adolescent Sexual Abuse and other socio-economic problems are detrimental for their mental health.
Emotional disorders are common in adolescents
Adolescence is an age when Emotional distress is very common. Depression, anxiety, excessive irritability, frustration, or anger are some symptoms which are commonly encountered in them. There may be rapid and unexpected changes in mood and emotional outbursts and many may complain of stress related physical disorders stomach ache, headache, or nausea.. Such youth can feel segregated and alone and can be so depressed that they can contemplate suicide.
Globally, depression is spreading like an epidemic and today it is considered to be the ninth leading cause of illness and disability among all adolescents whereas anxiety is the eighth leading cause. Depression can turn fatal and lead to suicide if not countered and addressed well in time.
Childhood behavioral disorders can pass on into adolescence. Childhood behavioural disorders such as hyper-activity and inattention (such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder) or destructive or challenging behaviours (for example, conduct disorder) represent repeated, severe and non-age-appropriate behaviours and can sometimes land them on the wrong side of Law of the land.
 Eating disorders are very common in adolescents
Eating disorders are very common in adolescents
Eating disorders such as anorexia nervosa, bulimia and binge eating disorder are commonly seen in adolescence and young adulthood and are more common in females than males. They have a pattern by harmful eating behaviours such as restricting the intake of calories or binge eating. Anorexia Nervosa and Bulimia have a preoccupation of thinking of food, body shape or weight, and abnormal behaviours such as excessive exercise or vomiting to compensate for calorie intake.
Psychosis—we should be aware of it in adolescence
Disorders which include symptoms of psychosis most commonly emerge in late adolescence or early adulthood. Symptoms of psychosis can include hallucinations (such as hearing or seeing things which are not there) or delusions (including fixed, non-accurate firm beliefs). Experiences of psychosis can stigmatize the person and stop him from interacting with others or participate in school or daily activities.
Suicide and self-harm –so common in adolescents
According to WHO, It is estimated that 62 000 adolescents died in 2016 as a result of self-harm. Suicide is the third leading cause of death in older adolescents (15–19 years). Nearly 90% of the world’s adolescents live in low- or middle-income countries but more than 90% of adolescent suicides are among adolescents living in those countries.
Suicide attempts can be impulsive or associated with a feeling of hopelessness or loneliness which means they may be having chronic depression.
Risk-taking behaviours especially Substance Use (Drugs)–in adolescents
Youngsters are poor and maladaptive coping to the daily life stressors by the youth. These can harm the youth mentally as well as physically.
These may lead them to Substance Use , sexual-risk taking behaviors or rash driving. Not having adequate skills and awareness how to plan and manage their emotions, trying to gain acceptance by their peers and other factors such as poverty and exposure to violence in and around them or in their childhood can increase the likelihood of their engaging in risk-taking behaviours. Indulging in acts of violence is a risk-taking behaviour and can lead the youth to low educational attainment, injury, involvement with crime, or death. Interpersonal violence was ranked the second leading cause of death of older adolescent boys in 2016.
The need of the hour is Early detection and treatment
It is crucial to address the needs of adolescents with defined mental health conditions. As far as possible we should focus on the age old theme of Prevention being better than Cure. We should try to catch them as early as possible, educate them, empower them and help them adopt healthy coping skills. We should avoid over-medicalization, and try to adopt measures prioritizing non-pharmacological approaches. Interventions for adolescents should consider that not all mental health treatments require medicines Psycho education, Counseling and psychotherapy are also very useful tools.
Dr Sona Gupta
Editors Note The Take Home Message is that Parenting is a skill which needs to be constantly learned and updated. Parents should learn the art of understanding and bonding with their adolescent children. Adolescence is and age of emotional and physical upheaval and turmoil. Adolescents should be psycho-educated and taught healthy coping skills and their day to day problems should be treated em-pathetically by their parents teachers and school. Peers are an integral part of their life at this stage.



